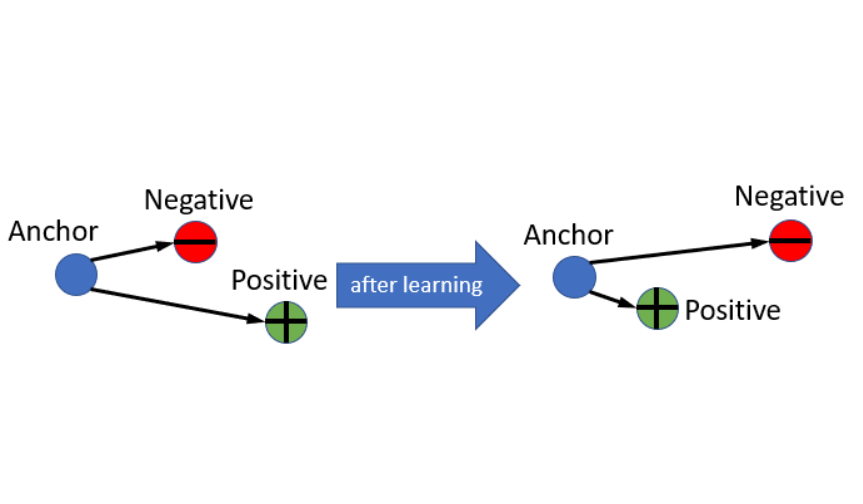
Triplet Loss Triplet Loss的介紹,相信在網路上已經有許多例子了,用途跟作用這邊就不多作介紹,將triplet的公式列出來,直接進入正題:
$$
{\mathcal{L_{triplet}}=\max{(\sum_{i=1}^N[||f^a_i - f^p_i||_2^2-||f^a_i - f^n_i||_2^2 + margin] ,\ 0)}}
$$
這邊會依序測試兩種不一樣的Triplet來計算Triplet Loss,分別是:
Batch Hard
Semihard
Sample Data 首先要先Sample出兩個不同的Embedding資料,直接使用numpy的random來產生兩個隨機的Embedding。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 import numpy as npbatch = 64 emb_dim = 1024 np.random.seed(1234 ) emb1 = np.random.rand(batch,emb_dim).astype(np.float32) np.random.seed(2345 ) emb2 = np.random.rand(batch,emb_dim).astype(np.float32) margin = 0.3 labels = np.arange(batch)
Triplet Loss (Batch Hard) 直接將最小的AN距離減掉最大的AP距離加上margin,此為Batch Hard的Triplet Loss。
Distance Metric 在Tensorflow Addons原始碼 中使用square再加起來等價於$XX^T$取對角的element,不過不確定跟目前使用的方法計算複雜度的差距:
1 2 3 4 5 xx = np.matmul(x, np.transpose(x)) xx = np.diag(xx) xx = tf.math.reduce_sum(tf.math.square(x), axis=[1 ], keepdims=True )
針對一個batch所有的資料兩兩計算,形成一個Batch*Batch的metric:
這裡計算每一筆的距離,回傳的是一個shape=(batch, batch)的metric:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 def np_distance_metric (embedding, squared=True ): """ Args: embedding: float32, with shape [n, d], (batch_size, d) Returns: dist: float32, with shape [m, n], (batch_size, batch_size) """ xy = np.matmul(embedding, np.transpose(embedding)) square_norm = np.diag(xy) xx = np.expand_dims(square_norm, 0 ) yy = np.expand_dims(square_norm, 1 ) distances = np.add(xx, yy) - 2.0 * xy ''' (batch_size,1)-(batch_size,batch_size): Equivalent to each column operation (batch_size,batch_size)+(1,batch_size): Equivalent to each row operation ''' distances = np.maximum(distances, 0.0 ) error_mask = np.less_equal(distances, 0.0 ).astype(np.float32) if not squared: distances = np.sqrt(distances + error_mask * 1e-16 ) distances = np.multiply(distances, np.logical_not(error_mask),) num_data = np.shape(embedding)[0 ] mask_offdiagonals = np.ones_like(distances) - np.diag(np.ones([num_data])) distances = np.multiply(distances, mask_offdiagonals) return distances
Mask _masked_minimum做的簡而言之就是將乘上mask後的data中根據dim取其最小值,具體步驟是:
首先將每筆資料對應的最大值選取出來,命名為:axis_maximums,將Distance Metric減掉這個最大值(axis_maximums),再乘上mask選取出需要比較的數值,接下來根據dim取出對應行或列中最小值,最後再將axis_maximum加回去就可以得到需要的結果,然後需要注意這邊有keepdims,所以會是(batch, 1)的形式。
具體的實現過程為:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 def np_masked_minimum (data, mask, dim=1 ): """Computes the axis wise minimum over chosen elements. Args: data: float32, with shape [n, m], (batch_size, batch_size) mask: boolean, with shape [n, m], (batch_size, batch_size) dim: int, the dimension which want to compute the minimum. Returns: masked_minimums: float32, with shape [n, 1], (batch_size, batch_size) """ axis_maximums = np.max (data, dim, keepdims=True ) masked_minimums = (np.min (np.multiply(data - axis_maximums, mask), dim, keepdims=True ) + axis_maximums) return masked_minimums
_masked_maximum做的事情和上面一樣,不過得到的為最大值:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 def np_masked_maximum (data, mask, dim=1 ): """Computes the axis wise maximum over chosen elements. Args: data: float32, with shape [n, m], (batch_size, batch_size) mask: boolean, with shape [n, m], (batch_size, batch_size) dim: int, the dimension over which to compute the maximum. Returns: masked_maximums: N-D `Tensor`. """ axis_minimums = tf.math.reduce_min(data, dim, keepdims=True ) masked_maximums = (tf.math.reduce_max(tf.math.multiply(data - axis_minimums, mask), dim, keepdims=True ) + axis_minimums) return masked_maximums
定義出以上function之後,就可以開始進行整個Triplet Loss的計算。
Batch Hard 首先先算出pairwise的距離矩陣pdist_matrix,再利用labels計算出row index和column index對應的embedding是否有相同的label(adjacency),相反可以得出不同的label(adjacency_not)。
如此就可以得到negative所在的mask和positive所在的mask,利用前面的mask function找出hardest的negative,同理利用前面的adjacency再去掉相同index的element就可以得到positive的mask,也就是得到hardest的positive。
有了hardest的positive跟negative就可以直接帶入triplet的公式:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 def np_triplet_batch_hard (labels, embedding, margin, soft ): ''' batch all triplet loss of a batch ------------------------------------ Args: labels: Label Data, shape = (batch_size,1) embedding: embedding vector, shape = (batch_size, vector_size) margin: margin, scalar soft:: use log1p or not, boolean Returns: triplet_loss: scalar, for one batch ''' lshape = np.shape(labels) labels = np.reshape(labels, [lshape[0 ], 1 ]) pdist_matrix = _distance_metric(embedding, squared=True ) adjacency = np.equal(labels, tf.transpose(labels)).astype(np.float32) adjacency_not = np.logical_not(adjacency).astype(np.float32) hard_negatives = _masked_minimum(pdist_matrix, adjacency_not) batch_size = np.size(labels) mask_positives = adjacency - np.diag(np.ones([batch_size])) hard_positives = _masked_maximum(pdist_matrix, mask_positives) if soft: triplet_loss = np.log1p(np.exp(hard_positives - hard_negatives)) else : triplet_loss = np.maximum(hard_positives - hard_negatives + margin, 0.0 ) triplet_loss = np.mean(triplet_loss) return triplet_loss
Triplet Loss (Semi-Hard) 前面定義出了Batch Hard的Triplet Loss是怎麼運作的,接下來要介紹什麼是Semi-Hard的Tirplet,簡而言之就是要找那些AN>AP但<margin的pair。
這裡分成5個部分來分別介紹。
Distance Metric 和前面一樣先計算出pdist_matrix,和相應的adjacency mask跟adjacency_not mask:
1 2 3 4 pdist_matrix = _distance_metric(embedding, squared=True ) adjacency = np.equal(labels, tf.transpose(labels)).astype(np.float32) adjacency_not = np.logical_not(adjacency).astype(np.float32)
negatives_outside 將pdist_matrix複製batch次,會得到pdist_matrix_tile,其shape為(batch*batch, batch),這是為了之後要挑出Semi-Hard的triplet pair而計算:
1 pdist_matrix_tile = tf.tile(pdist_matrix, [batch_size, 1 ])
同樣將adjacency_not複製batch次,並且將pdist_matrix根據row展開成一列其shape為(batch*batch, 1),讓pdist_matrix_tile中每一個element依序和展開的pdist_matrix相比,大於為Ture、反之False,最後再和batch倍的adjacency_not(為negative的所在)做and運算,例子如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 ''' np.reshape(np.transpose(pdist_matrix), [-1, 1]) ------------------------------------ ex. pdist_matrix = [[ 0. 11. 11.] [11. 0. 24.] [11. 24. 0.]] 轉換成(batch*batch,1): [[ 0.], [11.], [11.], [11.], [ 0.], [24.], [11.], [24.], [ 0.]] 依序和展開的`pdist_matrix`相比 np.greater(pdist_matrix_tile, np.reshape(np.transpose(pdist_matrix), [-1, 1])) ------------------------------------ [[False True True] [False False True] [False True False] [False False False] [ True False True] [False False False] [False False False] [False False False] [ True True False]] np.logical_and(a, b) ------------------------------------ [[False True False] [[False True True] [[False True False] [ True False True] [False False True] [False False True] [False True False] [False True False] [False True False] [False True False] [False False False] [False False False] [ True False True] and [ True False True] = [ True False True] [False True False] [False False False] [False False False] [False True False] [False False False] [False False False] [ True False True] [False False False] [False False False] [False True False]] [ True True False]] [False True False]] ''' a = np.tile(adjacency_not, [batch_size, 1 ]) b = np.greater(pdist_matrix_tile, np.reshape(np.transpose(pdist_matrix), [-1 , 1 ])) mask = np.logical_and(a, b)
這邊將pdist_matrix中的batch*batch展開,將每一筆當作AP和對應的row去比較(第一筆為row 1對column 1的距離,讓他對第一個row比較,如下圖),所以這邊評估在每個row中哪些比他本身更大,更大的作為True。
(1.1對1.all比較,1.2對2.all比較,…
接下來透過tile過的adjacency_not,把屬於不同label並且距離大於AP(pdist_matrix中每個element)的都挑選出來了。
接合前面的np_masked_minimum function我們可以得到AN的Semi-Hard的候選清單,也就是AN>AP的情況下最小的AN:
1 2 3 4 5 negatives_outside = np.reshape( np_masked_minimum(pdist_matrix_tile, mask), [batch_size, batch_size] ) negatives_outside = np.transpose(negatives_outside)
negatives_inside 以上滿足了AP<AN的狀況下找尋可計算pair,但有可能會存在AN<AP的時候,這個時候要找最遠的AN,和AP比較,也就是easy negatives:
1 2 negatives_inside = np.tile(np_masked_maximum(pdist_matrix, adjacency_not), [1 , batch_size])
semi_hard_negatives 將前面的mask,也就是AN>AP的情況下是否擁有的AN,做reduce_sum。換句話說就是將AN>AP的狀況下存在AN的element為True (也就是semi-hard的部分),使用negatives_outside的距離,反之用negatives_inside:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 ''' np.where(condition, x, y): if condition: return x else: return y ''' mask_final = np.reshape(np.greater(np.sum (mask.astype(np.float32), 1 , keepdims=True ),0.0 ), [batch_size, batch_size]) mask_final = np.transpose(mask_final) semi_hard_negatives = np.where(mask_final, negatives_outside, negatives_inside)
最後在滿足mask_final的情況下選擇negatives_outside和negatives_inside,作為AN來計算Triplet Loss,得到loss_mat。
Semi-Hard Triplet 因為在對角線部分為anchor對anchor的距離,這邊需要將它過濾掉,因為不是這邊需要的,所以算出label相同的mask之後減掉對角線,就可以找到positive的位置,將前面的loss_mat乘上這邊的mask,算總和後除以positive數量,就可以得到最後的triplet loss:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 loss_mat = np.add(margin, pdist_matrix - semi_hard_negatives) mask_positives = adjacency.astype(np.float32) - np.diag(np.ones([batch_size])) num_positives = tf.math.reduce_sum(mask_positives) triplet_loss = tf.math.truediv( tf.math.reduce_sum( tf.math.maximum(tf.math.multiply(loss_mat, mask_positives), 0.0 ) ), num_positives, )
Code Link 以上所有的code都是在Google Colab上面執行,版本為2.2.0。
Github:NeuralNetwork-01 Batch Hard and Semi-Hard Triplet Loss
參考資料 Triplet-Loss原理及其实现